With today’s ever-increasing demand for quickly-produced manufactured goods, there is a need to create the gears utilized to run various equipment in numerous sizes and which can operate with the highest degree of accuracy. Read More…
At Kager Industries, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for broaching, tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clientele. With years of experience and expertise in the industry, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader in precision machining, renowned for our commitment to excellence, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
At Broaching Industries, Inc., we dedicate ourselves to precision metalworking through advanced broaching techniques that deliver consistent, repeatable results for customers across diverse industries. We have built our reputation on the ability to produce complex internal and external profiles with tight tolerances, clean finishes, and efficient production times.

At Perry Technology Corporation, we take pride in our deep expertise in precision broaching and advanced manufacturing solutions. Over the years, we have built our reputation on delivering exceptional quality and consistency to industries that demand tight tolerances, complex geometries, and uncompromising performance.
More Gear Hobbing Companies
Gear hobbing is the process of creating gear teeth through a “hob,” which is a rotating cutter. This process may be used for either high or low volume production of external cylindrical gears. The production rate of gear hobbing is relatively high compared to other gear-making techniques. The method can be used to make spur, helical, worm, sprocket, and spline gears, among other types of gears.
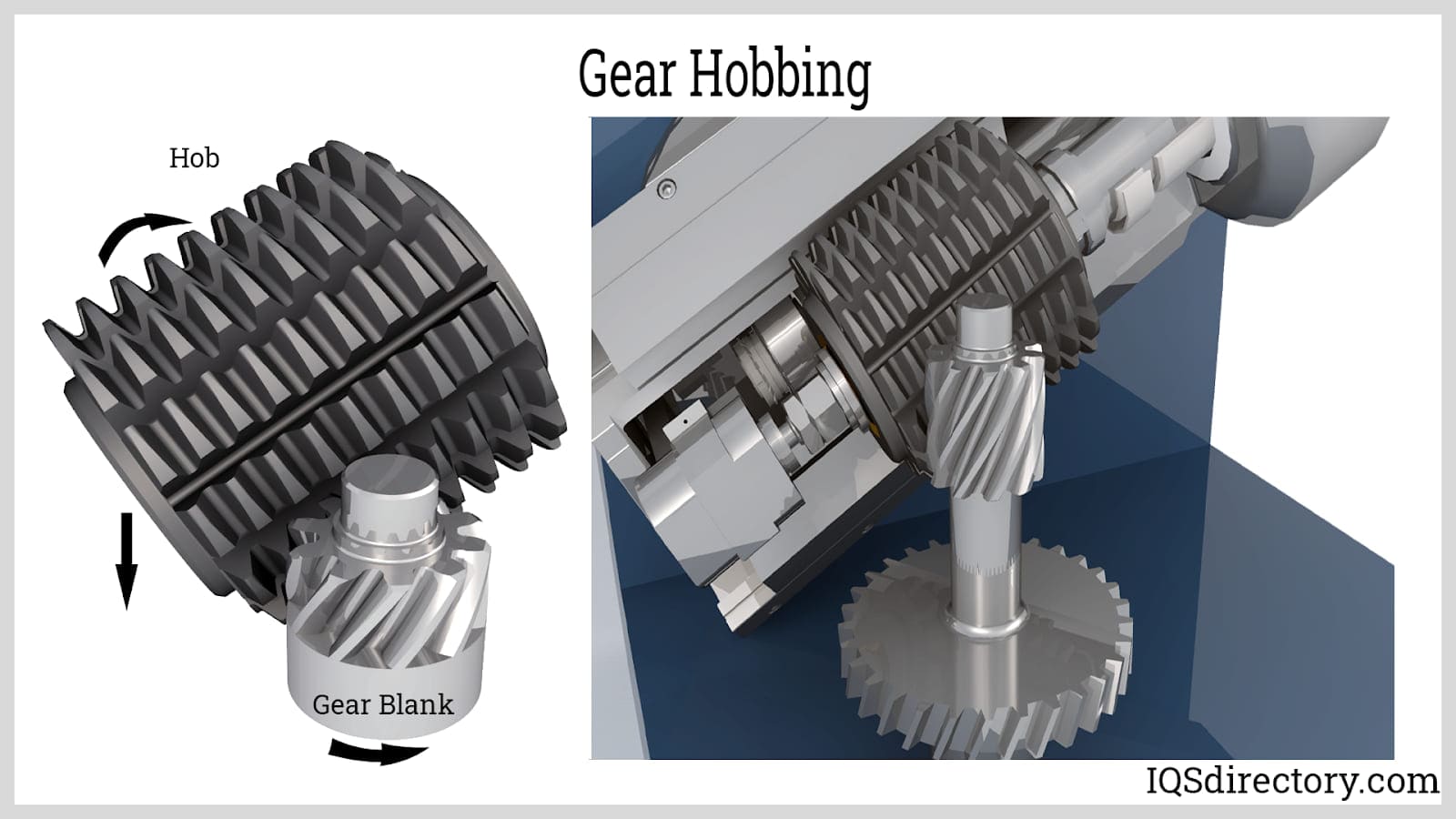
The Gear-Hobbing Process
Gear hobbing is a multi-step process. In the first step, a spinning cutter known as a hob is used to roll a gear blank. A multipoint cutting tool is then used. This tool resembles a worm gear with several straight flutes running parallel to its axis all around its circumference. These flutes are fashioned in such a way that they serve as cutting edges after being provided the correct angles. Next, the hob is fed to the gear blank while rotating at an appropriate rpm. The gear blank and gear hob's rpm are synced such that for every gear bob revolution, the gear blank rotates by a distance equivalent to one pitch of the gear that needs to be cut. This synchronization ensures that both the hob and the gear blank move consistently and steadily. In order for the hob's cutting blades to stay square with the gear blank during operation, it is tilted at a helix angle; the hob teeth then act like screw threads. A wide range of gears, including spur gears, helical gears, hearing-bone gears, splines, and gear sprockets, are made by gear hobbing.
Hob Positioning for Various Gears
After simultaneously spinning the gear blank and the cutter, known as a hob, with a fixed gearing ratio between the two, gears are cut. The gear blank is fed into the rotating hob until the necessary depth is obtained. Until all of the teeth are formed, the hob is fed across the blank's face. The hob teeth in a hobbing spur gear are positioned parallel to the blank's axis of rotation. Conversely, the axis of the hob is placed over an angle to create the proper helix for helical teeth bobbing. Worm gears, meanwhile, are made with the hob's axis fixed at a proper angle to the blank gear.
Techniques Used in the Hobbing Process
- Conventional hobbing: in this technique, the direction of the “feed (the moving direction of the hob in relation to the face of the workpiece)” matches the direction of the cutting motion. This technique produces a better finish but creates more wear.
- Climb hobbing: this technique has the feed in a direction opposite to the cutting motion. This technique is employed as a means to extend the tool’s life.
Hobbing Gear Parameters
Indexing movement, feed rate, and the angle between the axis of the gear blank and the gear hobbing tool are three crucial variables that must be under control (gear hob).
Hobbing Process Types
According to the hob's feeding directions for cutting gears, the gear- hobbing operation is divided into many groupings including axial feed, radial feed, and tangential feed categories as discussed below.
Gear Hobbing Using Axial Feed
In this procedure, the gear hob is fed against the gear blank parallel to its axis and along the blank's face. Gears like spur and helical gears are made using this operation.

Gear Hobbing Using Radial Feed
With this technique, the axes of the hob and gear blanks are arranged to be parallel to one another. The rotating hob is fed against the gear blank in a radial direction or perpendicular to the axis of the gear blank. Worm wheels are created using this process when the hob is positioned at the whole depth of the tooth and fed axially forward to the face of the gear blank; the hob is fed tangentially.

Gear Hobbing Using Tangential Feed
The teeth of a worm wheel are also cut using this method. The hob is held horizontally in this situation, with its axis oriented at the axis of the blank.

Benefits of the Gear-Hobbing Process
- When compared to other gear generation techniques, gear hobbing is an economical procedure since it is a quick and continuous operation.
- Its shorter manufacturing cycles results in a higher output rate.
- This process helps to create a wide range of gears, including worms, helical gears, spur gears, splines, and sprockets.
- By employing a method known as necessary indexing, the gear-hobbing process is relatively straightforward and able to produce any number of teeth while maintaining the module's accuracy.
- Gear hobbing alone can produce a specific kind of gear known as a herringbone gear (a special gear with a herringbone, or repeating V, pattern).
- The gear-hobbing process can handle a wide range of batch sizes, ranging from tiny to huge volumes.
- The gear-hobbing process makes it possible to process multiple gear blanks placed on the same arbor at once.
- Since a hob is a multipoint cutting tool with several cutting teeth or edges in itself, there are fewer cutting edges operating at once and there is more time for any heat created during this manufacturing process (and which may negatively affect the parts created) to be dissipated.
Drawbacks of the Gear-Hobbing Process
- The process is generally used to create external gears and typically requires additional setup for producing internal gears. Additionally, the machine must have the ability to fit a particular head for this purpose.
- The process cannot create bevel gears.
- There are size limitations regarding the gears it can produce.
- Producing splines or sprockets will require additional time to set up the machine to properly function.
Choosing the Proper Gear Hobbing Company
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing Gear Hobbing from a Gear Hobbing Supplier, it is important to compare at least 4 Companies using our Gear Hobbing directory. Each Gear Hobbing Company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Gear Hobbing business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Gear Hobbing companies with the same form.






 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services