Rotary broaching, also known as wobbling broaching, is a unique, quick, fantastic, and exact method of creating internal and exterior polygon forms on the end of a workpiece. The conventional broaching method entails inserting successively larger polygonal or other shapes into a hole until the desired form size is attained. By cutting the entire form, one corner at a time, rotary broaching can accomplish this in a single pass, frequently removing the need for a subsequent operation. This process works incredibly well on machines with horizontal or vertical spindles such as lathes, mills, etc. Read More…
At Kager Industries, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for broaching, tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clientele. With years of experience and expertise in the industry, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader in precision machining, renowned for our commitment to excellence, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
At Broaching Industries, Inc., we dedicate ourselves to precision metalworking through advanced broaching techniques that deliver consistent, repeatable results for customers across diverse industries. We have built our reputation on the ability to produce complex internal and external profiles with tight tolerances, clean finishes, and efficient production times.

At Perry Technology Corporation, we take pride in our deep expertise in precision broaching and advanced manufacturing solutions. Over the years, we have built our reputation on delivering exceptional quality and consistency to industries that demand tight tolerances, complex geometries, and uncompromising performance.
More Rotary Broaching Companies
Internal polygon structures can be quickly and precisely created using the rotary broaching technique—a highly efficient metalworking process renowned for its speed and accuracy. The entire rotary broaching process can be finished in a matter of seconds, and forms can be produced with an accuracy of at least 0.0005′′. This cutting-edge engineering approach has become increasingly popular, particularly in the plumbing, automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing sectors. Rotary broaching is the best technique for inserting a polygon form into the end of a part without the requirement for a secondary operation, making it an ideal solution for high-volume production, rapid prototyping, and demanding precision engineering applications.

What is Rotary Broaching? Understanding the Rotary Broaching Process
Rotary broaching, also known as wobble broaching, is a machining process used to create non-circular, precision internal and external polygonal shapes—such as hexagons, squares, and splines—inside or outside a workpiece. The process relies on a specially designed broach tool and a tool holder that allows the broach to rotate at a slight angle to the workpiece axis. As the rotary broach is pressed into the material, it produces highly accurate, repeatable forms in seconds—without the need for secondary finishing or deburring in most cases.
This broaching method is ideally suited for producing features such as:
- Hexagonal socket heads for fasteners
- Square drive recesses
- Torx, double square, and other custom polygonal forms
- Internal and external splines
- Medical implant recesses
- Precision features in aerospace components
Looking to understand if rotary broaching is right for your application? What geometric shapes can be produced with rotary broaching? How does the process compare to conventional broaching or EDM? Explore below for answers and essential decision criteria.
Requirements for the Rotary Broaching Process: What Equipment Do You Need?
Any conventional turning machine or milling machine can essentially be converted into a rotary broaching machine. All that is required are the following two key pieces of equipment:
- Rotary broach: The precision cutting tool used to cut a specific shape into, or remove a specific area from, a workpiece. Rotary broaches are manufactured in various standard and custom profiles to suit your application, with high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and specialty coatings available for extended tool life.
- Rotary broach tool holder: This specialized holder contains a mechanism that secures the broach in place and allows the spindle to rotate freely. The tool holder is engineered with a live spindle that tilts the broach at a precise angle (typically 1°) relative to the workpiece axis, enabling the unique wobbling action that defines the rotary broaching process.
These components can be fitted to most modern and legacy CNC lathes, Swiss-type machines, screw machines, and vertical or horizontal milling machines. For optimal performance, ensure your tooling and holders are compatible with your machine’s spindle and feed capabilities.
Machines That Use Rotary Broaching: Compatible Equipment and Setup
Rotary broaching is a versatile method that integrates seamlessly with a wide range of CNC machining and precision turning equipment. Here are some popular machines that are easily adapted to perform rotary broaching:
- CNC lathe machines: Ideal for high-volume, automated production of fasteners, medical implants, and custom components where internal or external features must be machined quickly and accurately.
- Swiss lathe machines: Suited for micro-machining and intricate parts with tight tolerances, such as those found in watchmaking, dental, and microelectronics industries.
- Milling machines: Both vertical and horizontal mills can accommodate rotary broaching tools, expanding the range of components and geometries that can be machined in a single setup.
- Screw machines: Perfect for high-throughput production of screws, bolts, and precision fasteners that require internal or external polygonal features.
Not sure if your current machine is compatible with rotary broaching? How can you retrofit your equipment for rotary broaching? What are the setup requirements for optimal performance? Contact a rotary broaching tooling supplier for a compatibility assessment and expert recommendations.
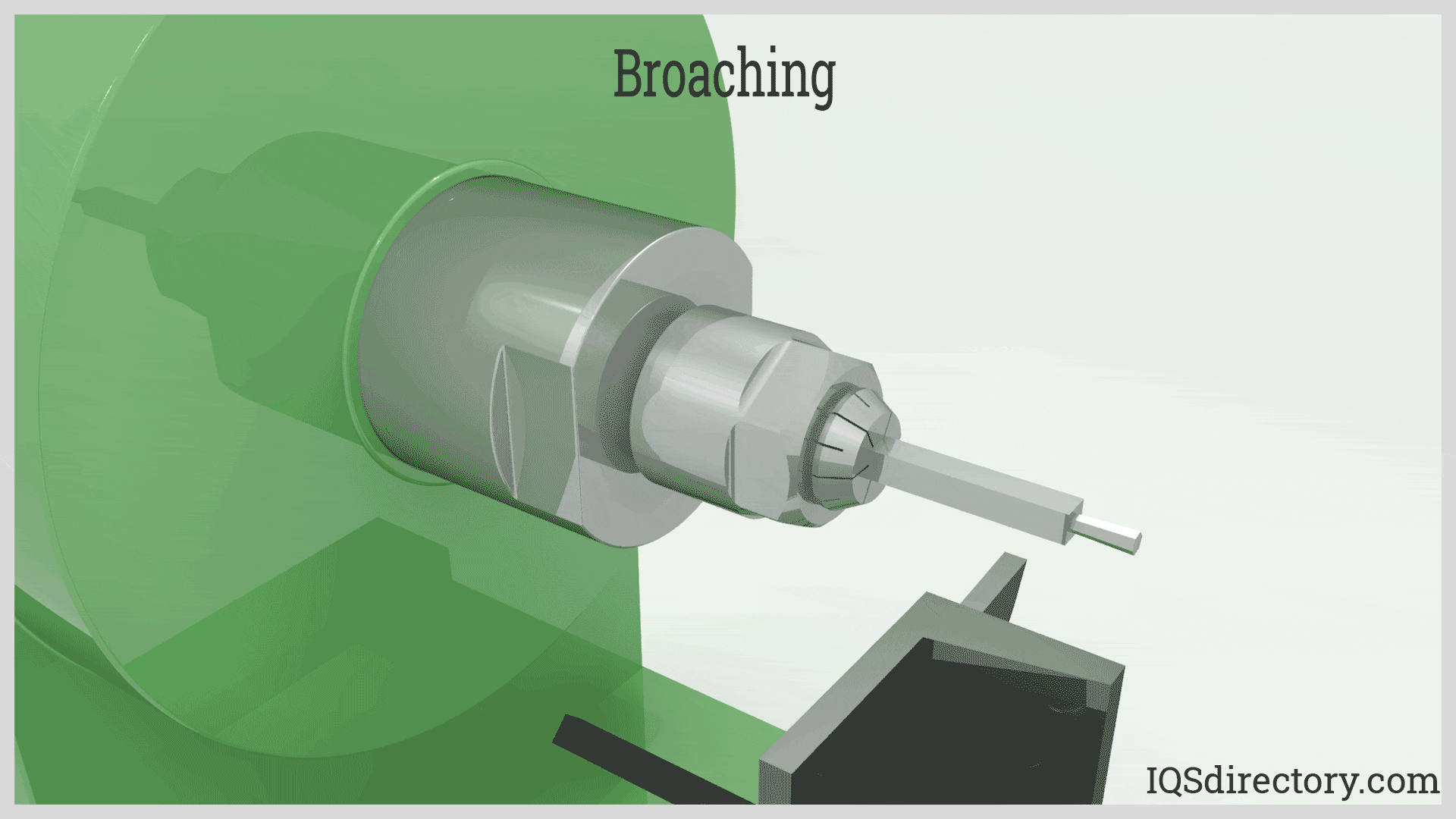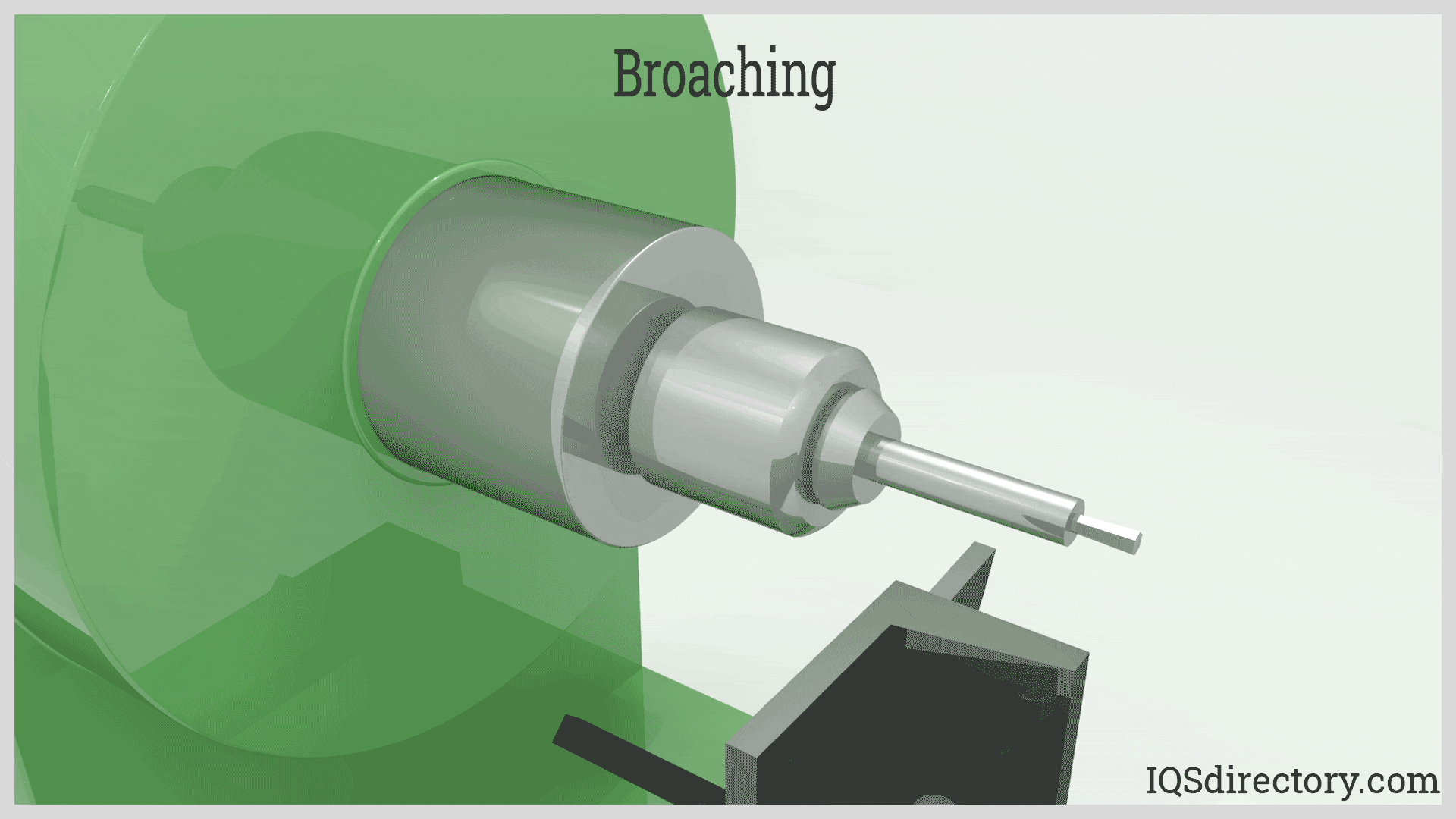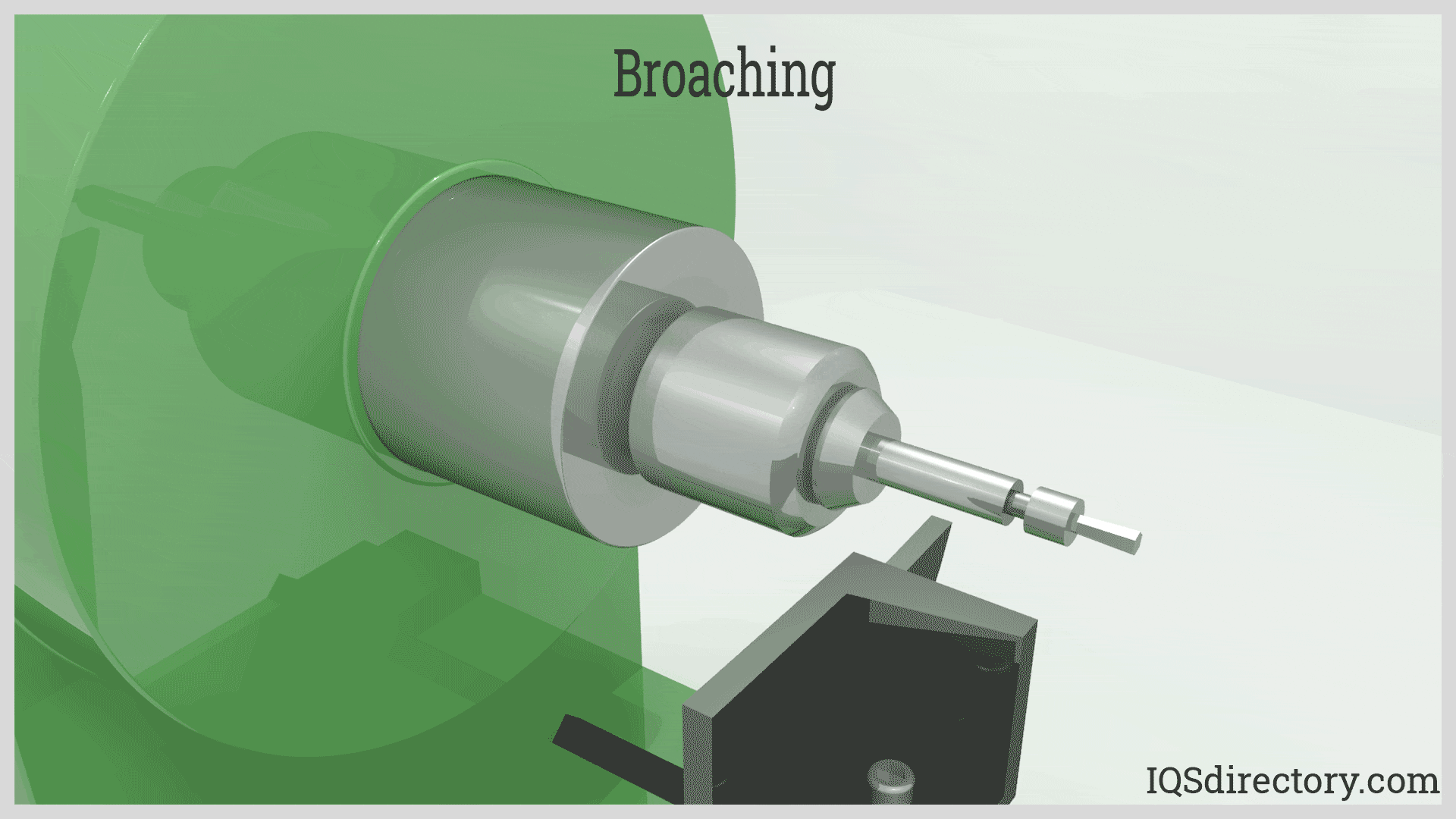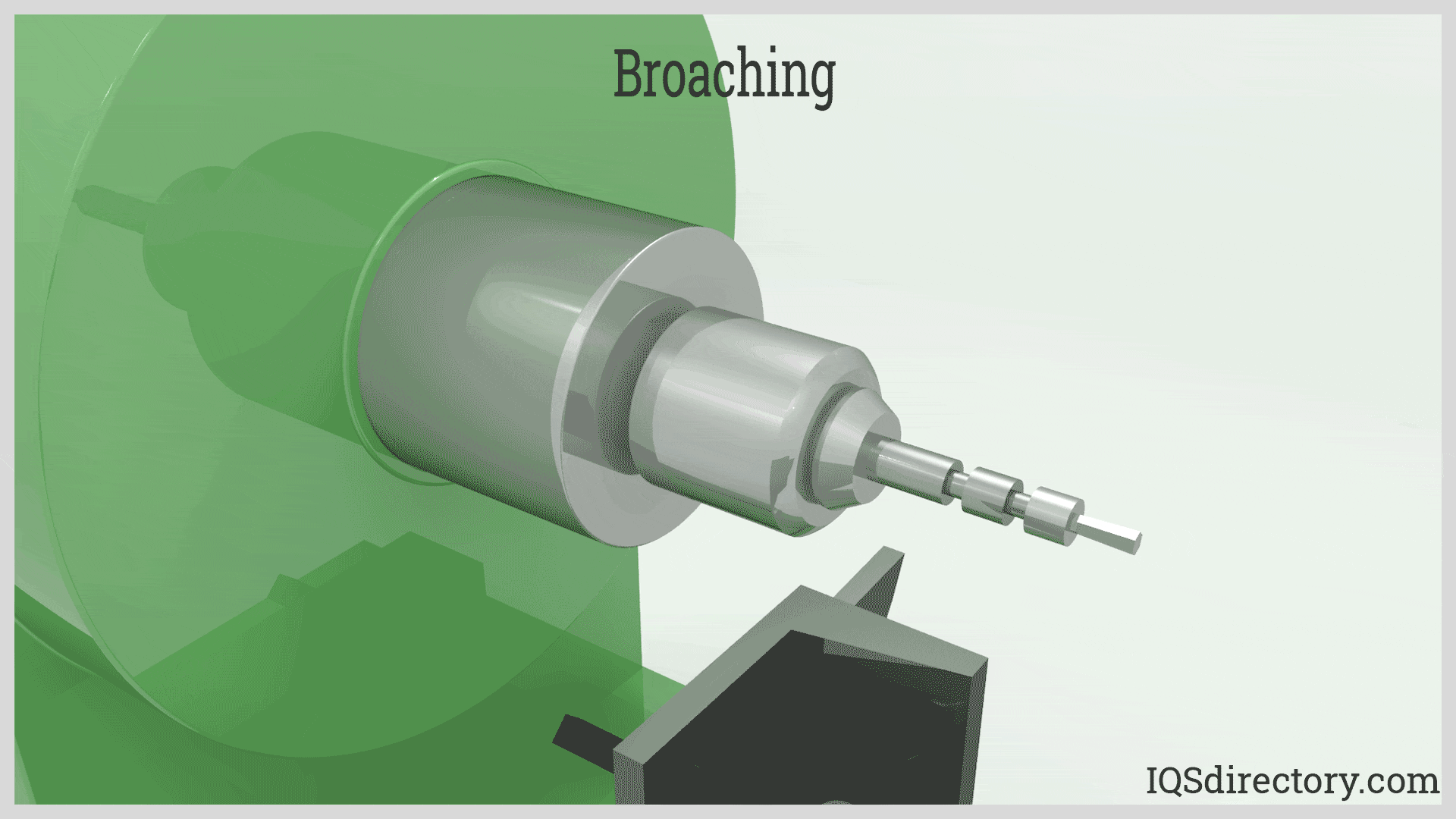
Working Principle of Rotary Broaching: How Does Rotary Broaching Work?
The core innovation behind rotary broaching lies in the unique interaction between the broach tool, the live spindle tool holder, and the rotating workpiece. Here’s how the process works step by step:
- The rotary broach is mounted at a slight angle (typically 1°) within the tool holder’s live spindle.
- The broach is positioned against the workpiece, which is rotating on a lathe or milling machine.
- As the workpiece rotates, the angled broach is pressed into it. The geometry of the holder causes the broach to "wobble," so only one corner of the tool is cutting at any given moment.
- This motion reduces cutting forces and thermal load, allowing for rapid material removal and precise formation of complex internal or external shapes.
- The broach advances along the axis of the part, producing a clean, dimensionally accurate feature in a single pass.
In a milling machine, the rotary broach tool and the internal live spindle of the tool holder remain fixed while the body of the tool holder revolves with the machine spindle. The constantly changing contact points between the broach’s corners and the workpiece result in a distinctive wobbling motion, producing smooth, high-quality finishes even on tough materials like stainless steel, titanium, and hardened alloys.
Wondering about broaching depth or material compatibility? How deep can you broach using rotary broaching? What materials are suitable for rotary broaching? Learn more in the application guidelines below.
1° Angle: The Key to Rotary Broaching Success
The secret to rotary broaching’s success is the cutting tool’s 1° angle relative to the midline of the workpiece. As the rotary broach is fed into the part to the required depth, it shears into the workpiece with a chisel or scalloping effect. The broaching tool remains securely held by a live spindle in the rotary broach tool holder, which allows the spindle to rotate freely within the holder. In a lathe, the spindle is propelled by contact with the rotating workpiece, minimizing setup requirements and streamlining the production process. Modern rotary broach tool holders feature sealed bearings that require minimal maintenance and a pressure relief hole to allow for air and fluid passage during broaching operations.

Rotating Spindle: Achieving High-Precision Polygonal Cuts
With rotary broaching, the broach is first inserted into a pre-drilled pilot hole in the workpiece. The workpiece is rotated by the spindle, while the broach holder spins in response, causing the broach to "wobble" as it advances. This dynamic motion facilitates the precise formation of internal and external polygonal shapes—critical for applications such as hex socket screws, medical device recesses, and advanced aerospace fasteners.
Need step-by-step guidance on setting up your machine for rotary broaching? What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances and smooth finishes? How do you select the right pilot hole size? Contact our technical experts or refer to our application resources for detailed setup instructions.
Cuts Each Corner Individually: Efficient Material Removal
Any turning machine equipped with a rotary broach tool can leverage this innovative process. As the broach is fed into the workpiece, the unique spinning motion causes it to wobble from corner to corner, concentrating the machine’s power on cutting just one corner at a time. This helical cutting pattern minimizes the forces on both the tool and the workpiece, allowing for efficient material removal, extended tool life, and reduced cycle times—even on small or delicate parts.
Precision Form: Achieving Unmatched Dimensional Accuracy
Rotary broaching yields extremely precise forms. Even though the tool is held at a one-degree inclination, the resulting feature’s dimensional accuracy matches the cutting tool’s geometry. Most rotary broaches are manufactured to a +0/-.0005" tolerance, ensuring that your finished parts meet or exceed stringent industry specifications. This high level of repeatability and precision is essential for mission-critical applications in aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing, where form, fit, and function are paramount.

Common Applications of Rotary Broaching: Where is Rotary Broaching Used?
Rotary broaching is widely used across a diverse range of industries due to its ability to produce complex shapes quickly and reliably. Typical applications include:
- Automotive manufacturing: Producing hex, square, and Torx drive features in fasteners, bolts, and custom components.
- Aerospace: Machining lightweight, high-strength fasteners and precision inserts with exacting tolerances.
- Medical devices: Creating intricate recesses in orthopedic implants, dental screws, and surgical instruments, where biocompatibility and precision are critical.
- Plumbing and hydraulic fittings: Forming internal and external polygonal recesses and drive features for reliable assembly and sealing.
- Electronics and micro-mechanics: Manufacturing miniature components with complex internal features, such as those used in connectors, switches, and micro-precision assemblies.
Searching for an industry-specific solution? How is rotary broaching used in medical device manufacturing? What benefits does rotary broaching offer for aerospace fasteners? Which industries benefit most from rapid, high-precision broaching? See our case studies or contact our specialists to learn more about application-specific advantages.
Advice Regarding Rotary Broaching: Best Practices for Success
To achieve the best results with rotary broaching, consider the following professional tips and guidelines:
- Ideal forming depth: The recommended broaching depth is typically up to 1.5 times the distance across flats (or the diameter of the inscribed circle) for the shape being produced. While deeper depths are possible, they may require specialized tooling and process optimization.
- Pilot hole sizing: Always drill a pilot hole slightly larger than the minor diameter of the broach profile to facilitate chip evacuation and reduce tool wear.
- Material selection: Rotary broaching is effective on materials such as aluminum, brass, stainless steel, titanium, plastic, and even some hardened alloys. However, tool life and finish quality can vary by material; choose broach material and coatings accordingly.
- Coolant and lubrication: Use appropriate cutting fluids or lubricants to minimize heat generation, improve chip removal, and extend broach life—especially when broaching tough or gummy materials.
- Tool holder maintenance: Select rotary broach holders with sealed bearings and pressure relief features to ensure long-term reliability and minimal maintenance requirements.

Have questions about setup or troubleshooting? What are the most common challenges in rotary broaching? How can you optimize tool life and performance? Our technical support team is available to assist with process optimization and problem-solving.
Benefits of Rotary Broaching: Why Choose Rotary Broaching for Your Project?
Rotary broaching offers a host of advantages over traditional broaching, EDM, and other non-circular hole-making and shaping techniques. Key benefits include:
- Fast, single-operation processing: Create complex internal or external shapes in seconds—often without secondary finishing or deburring.
- High accuracy and repeatability: Achieve precision tolerances of +0/-.0005", ensuring consistent quality for every part produced.
- Versatility: Suitable for a broad range of shapes (hex, square, Torx, spline, custom profiles) and materials, enabling flexible manufacturing solutions.
- Cost-effectiveness: After the initial investment in tooling and setup, maintenance costs are low and throughput is high—making rotary broaching ideal for both high-volume and short-run production.
- Reduced machine downtime: Minimal setup and tool change requirements mean less downtime and more productive machine hours.
- Minimal burr formation: The unique cutting action results in clean features that often require no additional finishing.
- Compact tooling footprint: Rotary broach holders and tools are compact and easy to integrate into existing machine setups, even in space-constrained environments.
Curious about cost savings or process efficiency? How does rotary broaching reduce production costs? Can rotary broaching replace secondary operations in your workflow? Contact us for a custom ROI analysis or process audit.
Rotary Broaching vs. Conventional Broaching: Which is Better for Your Needs?
While both rotary broaching and traditional push/pull broaching can produce similar features, there are important distinctions to consider:
- Rotary broaching is performed on lathes, mills, and screw machines, making it ideal for producing features in parts already being turned or milled. It excels in small-to-medium size part production, and offers rapid cycle times and lower setup costs.
- Conventional broaching (linear broaching) usually requires specialized broaching machines and is better suited for large or long parts, high-volume production of identical features, and very deep broached profiles.
Choosing between the two depends on your part geometry, material, production volumes, and available equipment. For most applications involving precision holes, recesses, or external features up to moderate depth, rotary broaching is the faster, more cost-effective solution.
How to Select the Right Rotary Broaching Supplier: Key Decision Factors
To ensure you achieve the best results when purchasing rotary broaching services or rotary broaching tools, it’s important to compare multiple suppliers. Here are important considerations to guide your decision:
- Experience and expertise: Look for suppliers with proven experience in your target industry—whether automotive, aerospace, medical, or general manufacturing.
- Tooling quality: Evaluate broach and holder material options, as well as precision, coatings, and availability of custom profiles.
- Support and engineering services: Choose a company that offers application engineering, troubleshooting, and technical support to optimize your process.
- Lead time and inventory: Assess supplier lead times, in-stock tooling availability, and flexibility for rush orders or custom solutions.
- Pricing and ROI: Compare pricing, but consider total cost of ownership—including tool life, maintenance, and productivity gains.
- Customer reviews and case studies: Review supplier references, case studies, and testimonials to gauge performance and satisfaction.
Use our comprehensive directory of rotary broaching suppliers to compare at least 4 or 5 companies. Each rotary broaching company profile includes details on their service capabilities, areas of specialization, and direct contact options. Use our proprietary website previewer to evaluate potential partners, then request multiple quotes using our convenient RFQ form for side-by-side comparison.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rotary Broaching
- What shapes can be made with rotary broaching? Most commonly, hex, square, Torx, and spline profiles, but custom forms are possible with bespoke tooling.
- Is rotary broaching suitable for hard materials? Yes, but tool material and coatings should be optimized for harder alloys to ensure tool life and surface finish.
- What is the maximum depth achievable? Typically up to 1.5 times the across-flats distance; deeper broaching is possible with specialized setups.
- Can rotary broaching be used for both internal and external features? Absolutely—while internal broaching is most common, external rotary broaching is used for features like splines, flats, and custom drive shapes.
- What maintenance is required for rotary broaching holders? Modern holders with sealed bearings are low-maintenance; periodic inspection and lubrication (if not sealed) are recommended for long service life.
Get Started with Rotary Broaching: Next Steps
Ready to integrate rotary broaching into your manufacturing process? Contact a specialist today to discuss your application, request a tooling quote, or arrange a process demonstration. Take advantage of our knowledge base, technical guides, and supplier directory to maximize your investment in precision broaching solutions.
Still have questions? What are the latest advancements in rotary broaching technology? How can you automate broaching operations for higher efficiency? Connect with our team for expert guidance, case studies, and the latest industry insights.






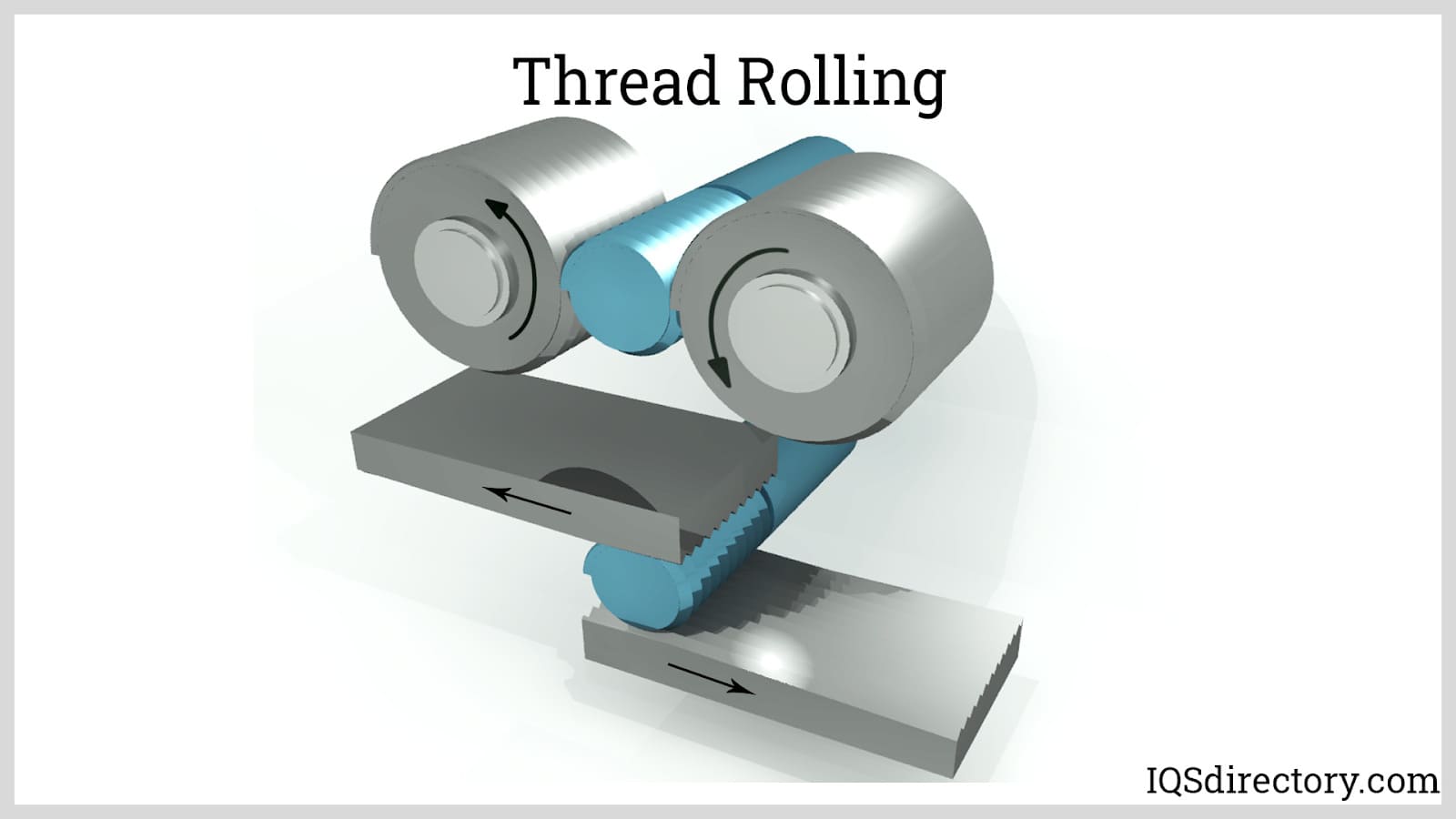
 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services